- Home
- About Us
- Students
- Academics
-
Faculty
- Electrical Engineering
- Automation
- Computer Science & Engineering
- Electronic Engineering
- Instrument Science and Engineering
- Micro-Nano Electronics
- School of Software
- Academy of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering
- School of Cyber Security
- Electrical and Electronic Experimental Teaching Center
- Center for Advanced Electronic Materials and Devices
- Cooperative Medianet Innovation Center
- Alumni
-
Positions
-
Forum
News
- · Bin Dai's Team Unveils the Assembly Mechanism of β-Lactoglobulin Fibrils, Providing New Insights for the Development of Functional Nanomaterials
- · Mingyi Chen’s research group has made important progress in the field of analog-to-digital converter chips for brain-computer interface
- · Progress in the Development of Semiconductor Nanomaterials to Activate Pyroptosis for Cancer Therapy
- · Jiamiao Yang’s team achieved the high precision optoelectronic reservoir computing based on complex-value encoding
- · Significant Advancements in Resonator-Enhanced Quantum Sensing Achieved by Zenguihua's Team at the School of Sensing Science and Engineering
Wang Kan's research group has published a review of wearable sensors in the Journal of Nanobiotechnology
Recently, the review "Ambient energy harvesters in wearable electronics: fundamentals, methodologies, and applications" by Associate Professor Wang Kan's team at the School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Shanghai Jiaotong University, was published in the Journal of Nanobiotechnology. This paper mainly focuses on the current mainstream wearable sensor power supply technologies, including the energy conversion mechanism, basic characteristics and typical application, so as to bring valuable reference for researchers in related fields.
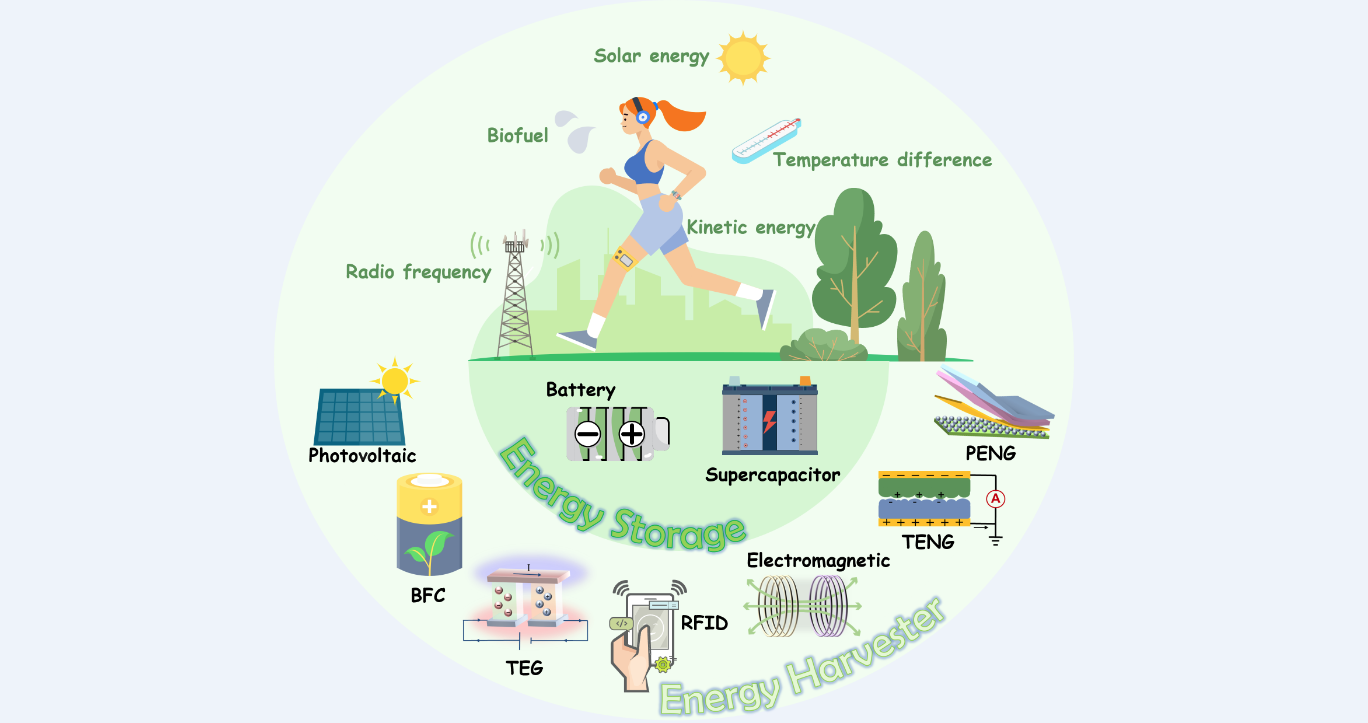
Figure 1 Various energy sources in life and the power supply technology of wearable sensing electronics
The background of this study:
Due to their capacity to continuously collect physiological data in real time, wearable sensors provide valuable insights to facilitate personalized health management and precision medical diagnosis. Whereas, demands for miniaturization, comfort, and user-friendly designs for wearable devices have become increasingly important in addition to pursuing functional diversity and superior performance, which are challenging problems for power supply module operation. Notably, nanomaterials and related technologies are significant in addressing power supply for wearable sensors: their unique electrical properties facilitate energy harvesting and storage, while high specific surface area and electrochemical activity enhance energy conversion at material interfaces, leading to widespread adoption in power modules of sensor systems in recent years.
Main content:
This paper comprehensively reviews the current mainstream energy technologies for powering wearable sensors, including supercapacitors, solar energy, biofuel cells, thermoelectric generators, radio frequency energy harvesters, and kinetic energy harvesters, as well as hybrid power systems that integrate multiple energy conversion modes. It delves into their energy conversion mechanisms, typical characteristics, and latest application advancements across various fields. These technologies not only propel wearable devices towards lighter, thinner, and longer-lasting designs but also significantly expand their applications in medical diagnosis, environmental monitoring, etc. Moreover, the crucial roles of different materials, such as nanomaterials and nano-processing techniques, in improving device performance is highlighted, thus bringing more possibilities for future developments in this field.
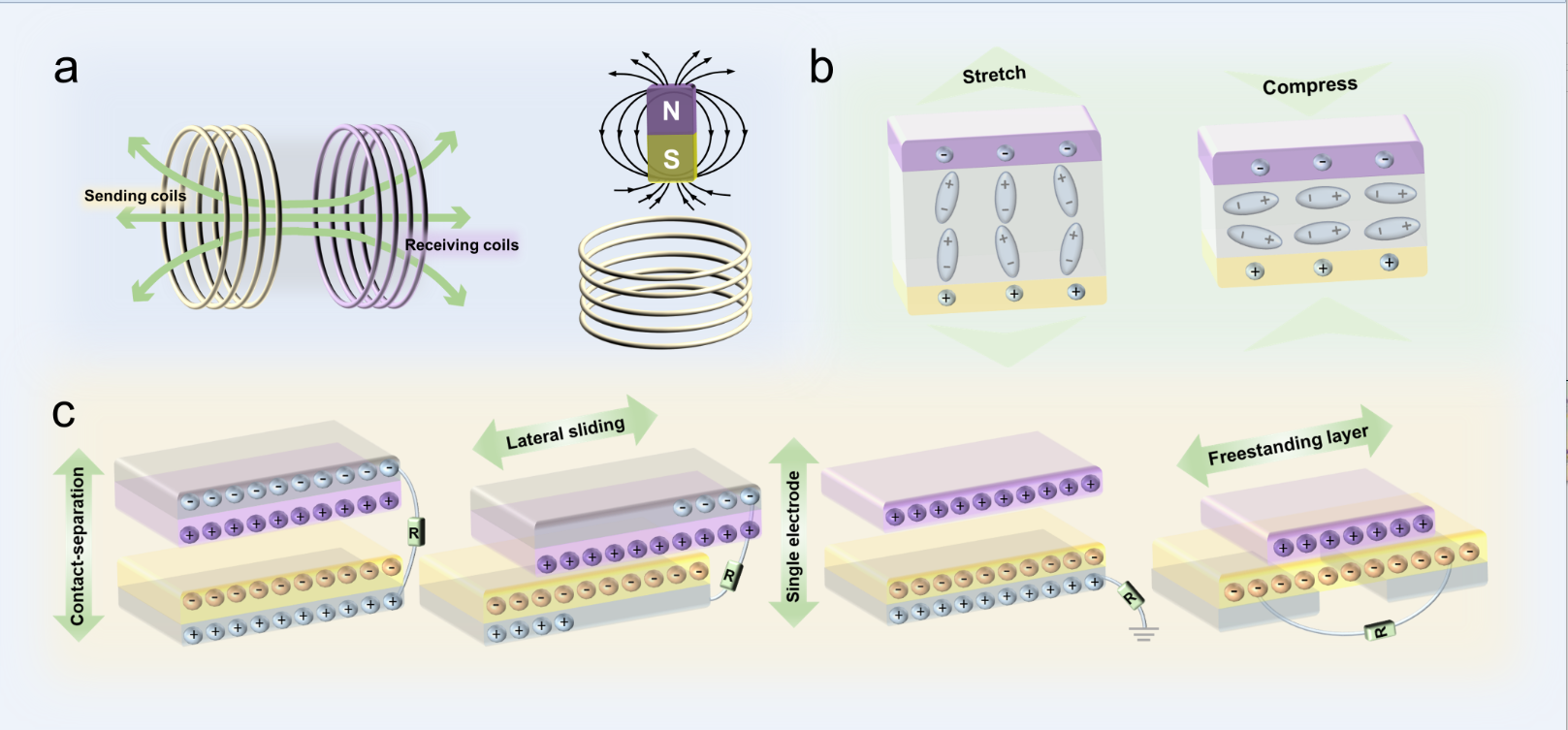
Figure 2 The working principle of (a) electromagnetic energy harvesters, (b) PENGs, and (c) TENGs
Conclusions and perspectives:
The paper concludes by summarizing the characteristics and suitable applications of various energy technologies. For instance, RF energy harvesters and NFC are immune to environmental factors like temperature and light, yet transmission distance and parameter matching are crucial design considerations. Meanwhile, challenges like performance degradation under complex body movements, synthesis and processing of nanomaterials, and production costs are pointed. At the end of the paper, it analyzes the future development direction of this field lies in miniaturization, digitalization and environmental friendliness. As system designs advance and energy technologies mature, wearable sensors will evolve rapidly, enhancing human health and lifestyles.
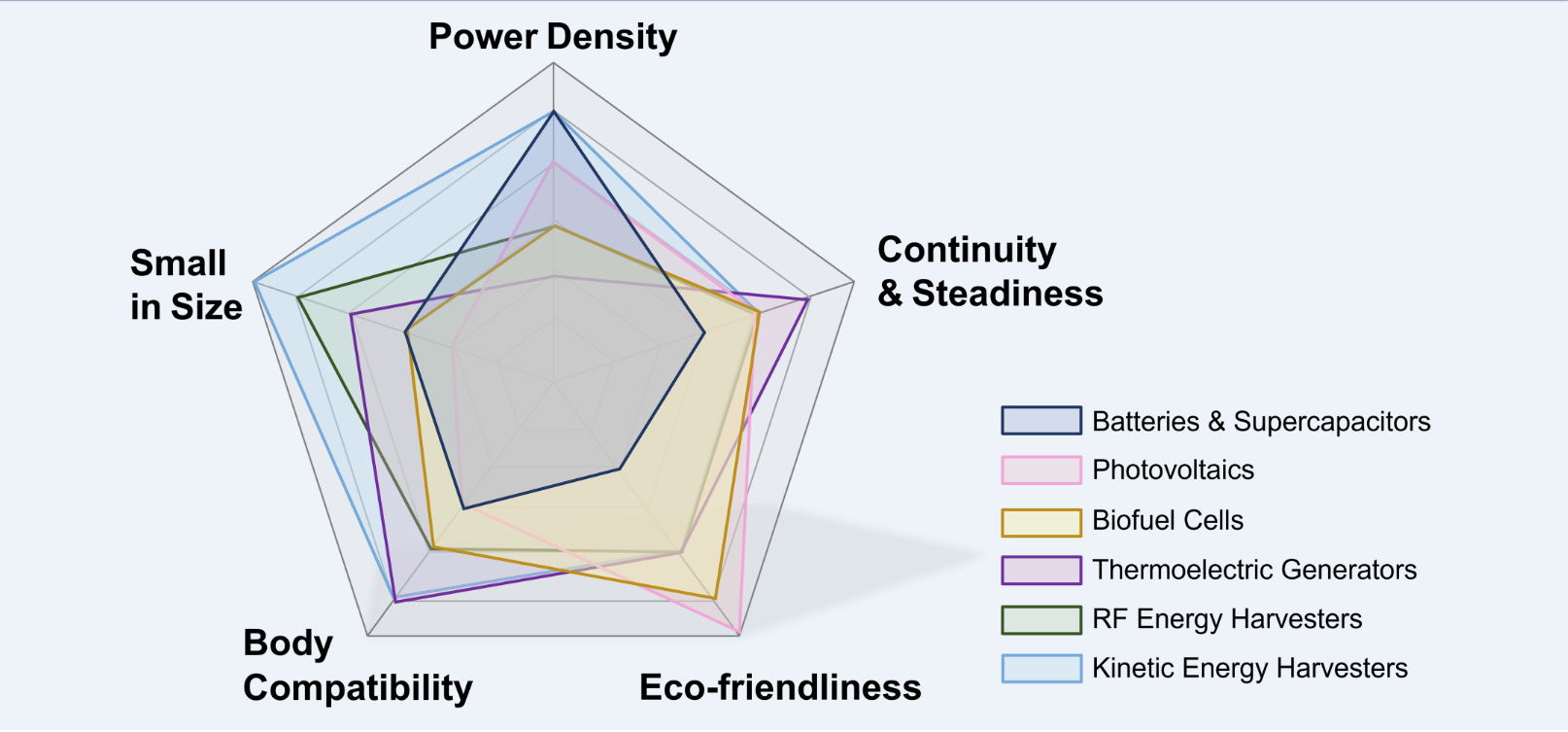
Figure 3 Multi-dimensional performance comparison of various power supply modes
The information of the paper:
Ruoyao Yu, a master's student at the School of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, and Shaoqing Feng, associate chief physician of the Ninth People's Hospital, were the co-first authors of the paper, and Kan Wang, an associate professor, was the corresponding author. This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2023YFF0724300), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32171373).
Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-024-02774-0
The information of the journal:
Journal of Nanobiotechnology is a journal focusing on the intersection of nanoscience and biotechnology, and mainly publishes articles related to bioengineering and applied microbiology and nanotechnology. This journal was founded in 2003, and the impact factor has gradually increased in recent years, which has reached 10.6 in 2023. The journal is in the Q1 region of the Chinese Academy of Sciences subdivision of biology and also in the Q1 region of the WOS subdivision.
-
Students
-
Faculty/Staff
-
Alumni
-
Vistors
-
Quick Links
